Chromatin Is the Complex of and Found Within Eukaryotic Chromosomes.
In the nucleus of eukaryotic cells chromosomes are arranged in a complex three-dimensional 3D architecture that is thought to be important to ensure the correct execution of gene expression. Although the control of gene expression is far more complex in eukaryotes than in bacteria the same basic principles apply.

Chromosomes Learn Science At Scitable
In some eukaryotic genes there are regions that help increase or enhance transcription.
. The nucleus is the most obvious organelle in any eukaryotic cell. The nucleoid meaning nucleus-like is an irregularly shaped region within the prokaryotic cell that contains all or most of the genetic material. Chromatin is a complex of macromolecules composed of DNA RNA and protein which is found inside the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
In prokaryotes the circular chromosomes are located in nucleoid which is present in the cytoplasm. DNA can be found arranged within chromosomes. Each eukaryotic chromosome is composed of DNA coiled and condensed around nuclear proteins called histones.
However the eukaryotic cell also contains non-nuclear genomes within the organelles. The mitochondrial genome within the mitochondrial matrix Figure 1. C Proper packaging and segregation of the replicated DNA must.
In eukaryotes the chromosome is stored inside the nucleus. Chromatin makes it possible for a number of cell processes. Within each nucleus is nuclear chromatin that contains the organisms genome.
They can be located upstream of a gene within the coding region of the gene downstream of a gene or may be thousands of nucleotides away. Transpliced genes are the exception to the rule for annotating gene feature spans. B Proper division of the cytoplasm must occur.
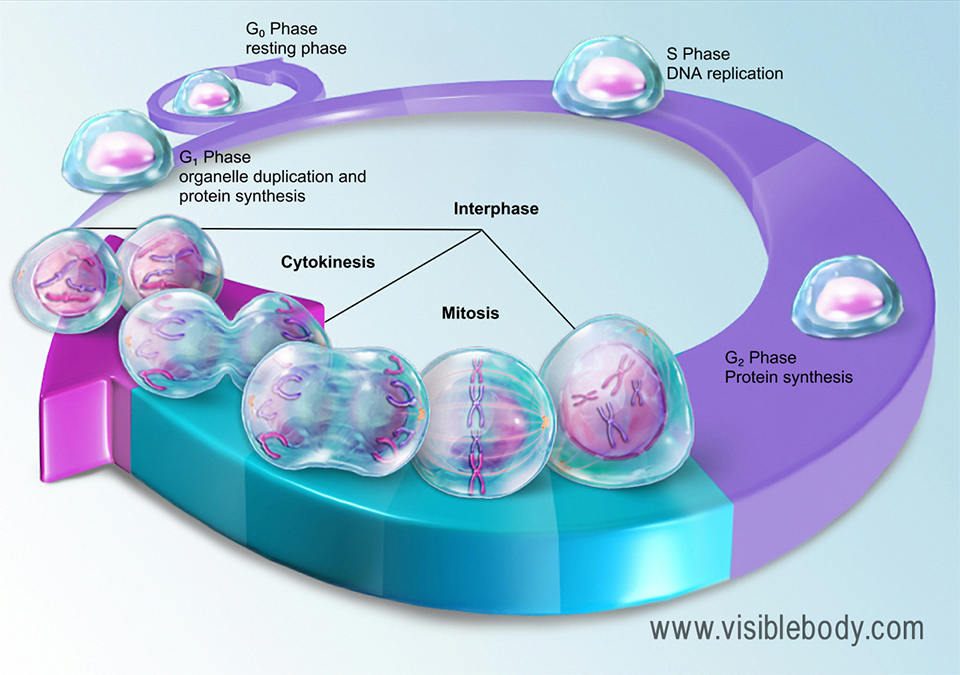
Learn how ancient collaborations between cells gave eukaryotes an important energy boost. The chloroplastic genome within the chloroplast stroma eg. In order for a eukaryotic cell to undergo reproduction and divide certain steps must be successfully completed.
A Replication of the DNA within the nucleus must occur. In eukaryotic cells the chromosomes are located in. It is usually this genome that is referred to when the genome of a eukaryote is mentioned.
The chromosome of a prokaryote is circular and its length is very large compared to the cell dimensions so it needs to be compacted in order to fitIn contrast to the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell it is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. 300 Function of DNA. Eukaryotes have many chromosomes and those chromosomes are enclosed in a nuclear envelope.
020 The Structure of Chromosomes. Eukaryotic cells contain greater amounts of DNA and this DNA is associated with various proteins. These regions called enhancers are not necessarily close to the genes they enhance.
Transpliced genes are similar to intron containing genes except the two pieces of the gene are found on different regions of the chromosome. Its prime function is packaging very long DNA molecules into a denser shape compact which stops the strands from becoming tangled and plays vital roles in strengthening the DNA during cell division avoiding DNA damage and controlling gene expression and DNA replication. It is enclosed in a double membrane and communicates with the surrounding cytosol via numerous nuclear pores.
A complex of DNA RNA and proteins within the cell nucleus out of which chromosomes condense during cell division Transcription through Nucleosomes Following the formation of the pre-initiation complex the polymerase is released from the other transcription factors and elongation is allowed to proceed with the polymerase. Chromosome - a long stringy aggregate of genes that carries heredity information DNA and. Chromatin - the mass of genetic material composed of DNA and proteins that condense to form chromosomes during eukaryotic cell division.
Learn about the organization of DNA within chromosomes. Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic ones because of specialized organelles. Select the choice below that is NOT one of these necessary steps.
In cell biology the spindle apparatus refers to the cytoskeletal structure of eukaryotic cells that forms during cell division to separate sister chromatids between daughter cellsIt is referred to as the mitotic spindle during mitosis a process that produces genetically identical daughter cells or the meiotic spindle during meiosis a process that produces gametes with half the number of. The diversity of cells in a multicellular eukaryote suggests that certain genes are active in some cells but not in others. Eukaryotic chromosomes consist of a DNA-protein complex that is organized in a compact manner which permits the large amount of DNA to be stored.
The expression of eukaryotic genes is controlled primarily at the level of initiation of transcription although in some cases transcription may be attenuated and regulated at subsequent steps. Chromatin is a complex of RNA DNA and protein can be seen in eukaryotic cells. Chromatin exists in two forms.
Heterochromatin condensed and euchromatin extended. As in bacteria transcription in eukaryotic cells is controlled by. The final packaging occurs when the fiber is organized in loops scaffolds and domains that give a final packing ratio of about 1000 in interphase chromosomes and about 10000 in mitotic chromosomes.
This page has. Chromatin fibers are coiled and condensed to form chromosomes. The chromatin is efficiently packaged within the small nuclear space.
These genes are transcribed as two or more separate RNA products that are transpliced into a single mRNA or tRNA.
The Structure And Function Of Chromatin

Chromosome Structure Biology For Non Majors I

Dna Packaging In Eukaryotes And Prokaryotes Biology For Majors I
0 Response to "Chromatin Is the Complex of and Found Within Eukaryotic Chromosomes."
Post a Comment